The volume of blood flowing back to the heart through the veinsDue to contracting of the left ventricle What are the 2 types of venous return pumps?GCSE High_School_Diploma Remember Veins have Valves text One way vein valve diagram, vein and artery circuit diagramsHuman Arterial And Venous Diagrammed Of The Veins Venous Ulcers Homework 1 True/false The medium and large veins in the leg have bicuspid valves to prevent retrograde venous blood flow, but the perforating veins do not have valves False 2 What causes the ulcers to form in patients with venous insufficiency?

Artery Wall An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Artery and vein diagram lumen
Artery and vein diagram lumen-GI radiological anatomy Abdominal vessels This has two modules Learning Module To review the content of the subject UNDER CONSTRUCTION Self assessment module You should use this module only after you have read textbooks or have knowledge of the subject and are ready to see whether you have comprehended the subjectThe pulmonary veins are included in the diagram because, like The tip, known as the apex, points downwards and lies close to the sternum Heart Anatomy Labeled Diagram Structures Blood Flow Function Of Cardiac System Ezmed from iytimgcom The largest artery in the body is the aorta, in the heartthe aorta receives blood from the heart's left ventricle, then branches off into
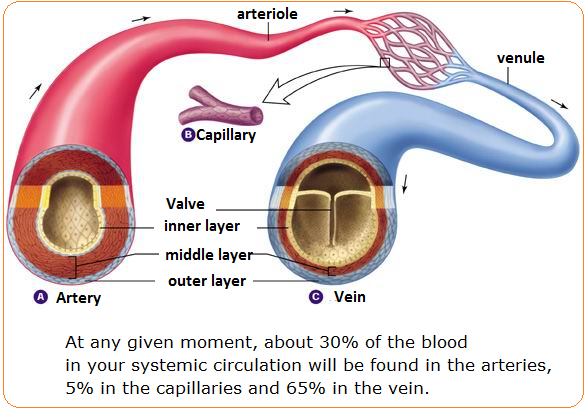



How Would You Compare The Structures And Functions Of Arteries Capillaries And Veins Socratic
Size of the lumen 2 Blood viscosity 3 Total blood vessel length What is venous return? Arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart, where it branches into even smaller vessels Finally, the smallest arteries, called arterioles are further branched into small capillaries, where the exchange of all the nutrients, gases and other waste molecules are carried out Veins are the blood vessels present throughout the bodyStart studying Chapter 19 diagram arteries and veins Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools
Digestive Absorbs nutrients and water;Start studying Artery and vein Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Search Create Log in Sign up Log in Sign up Artery and vein STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Adeline_Woodall Terms in this set (41) artery away from heart vein to heart artery has ____ wall thicker (smooth muscle,B The majority of both arteries and veins contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood;
Blood vessels are part of the cardiovascular system that transports blood throughout the human body There are three major types of blood vessels veins, arteries, and capillaries Figure 74 2 This figure shows the heart and the major arteries of the cardiovascular system The pulmonary veins are included in the diagram because, likeDelivers nutrients (except most lipids) to liver for processing by hepactic portal vein;The interior of the gastrointestinal tract;



Structure Lumen Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Vascular System 1 Anatomy And Physiology Nursing Times
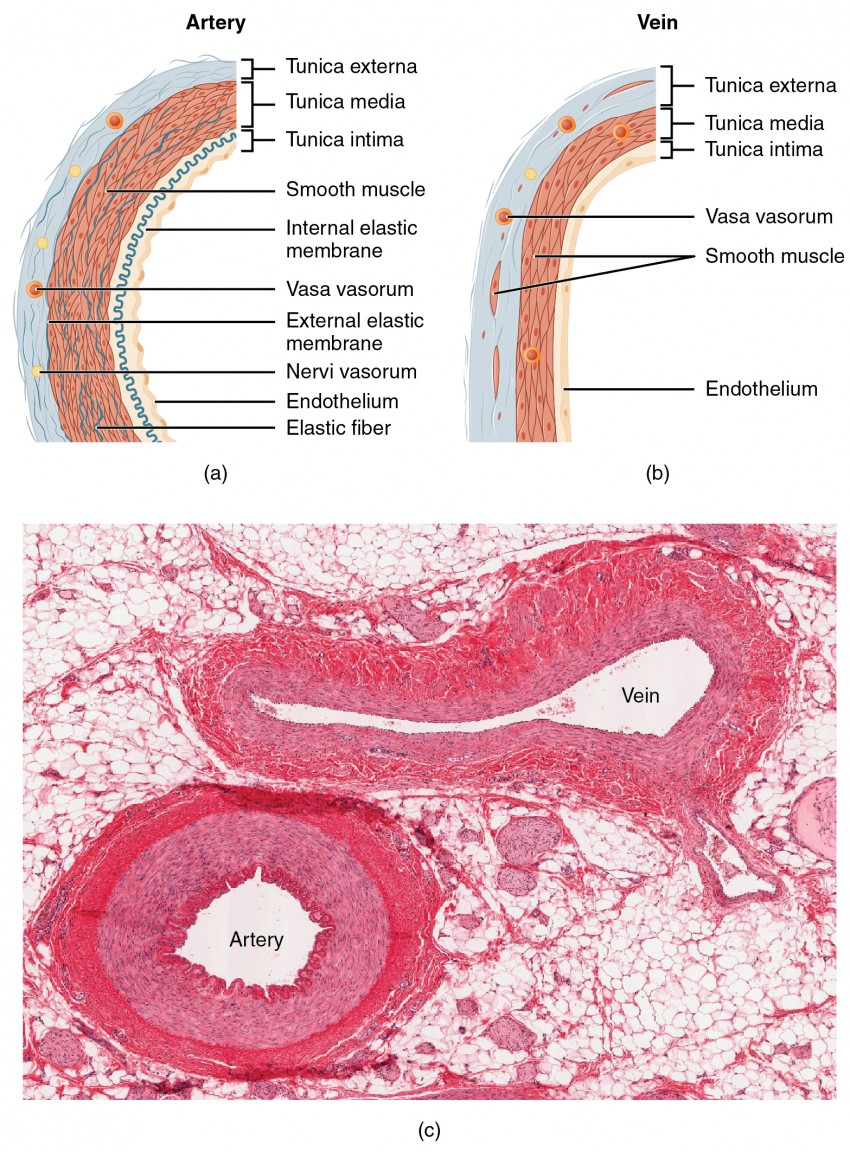
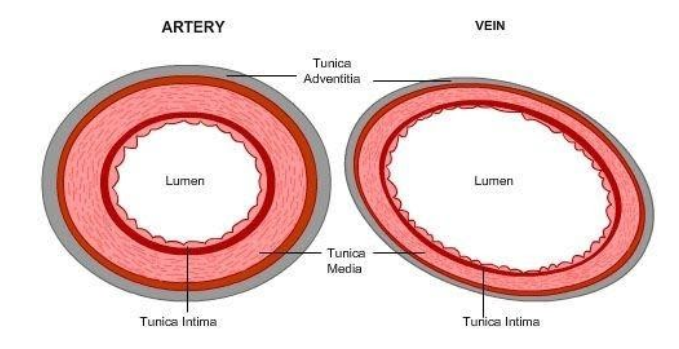
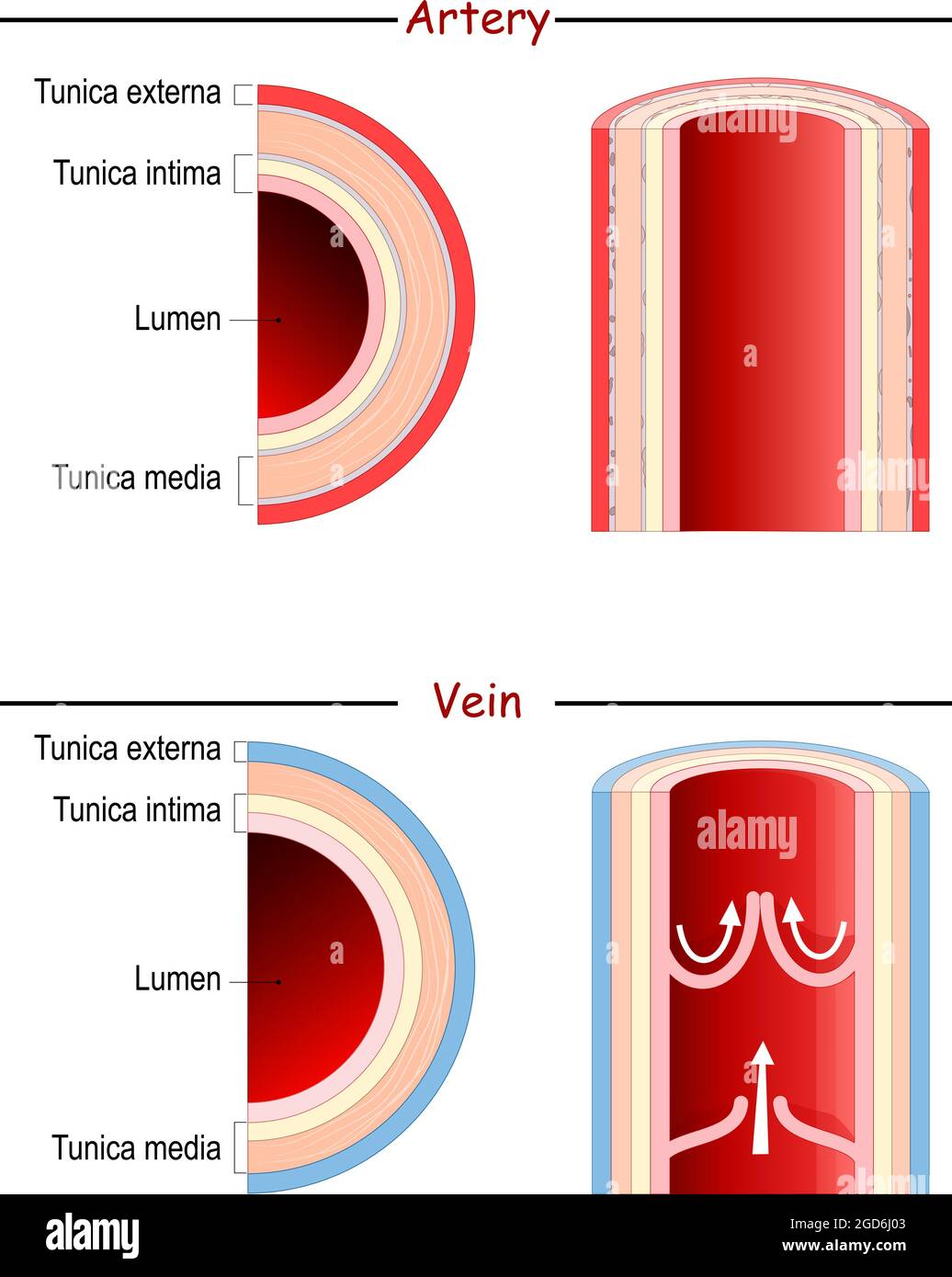
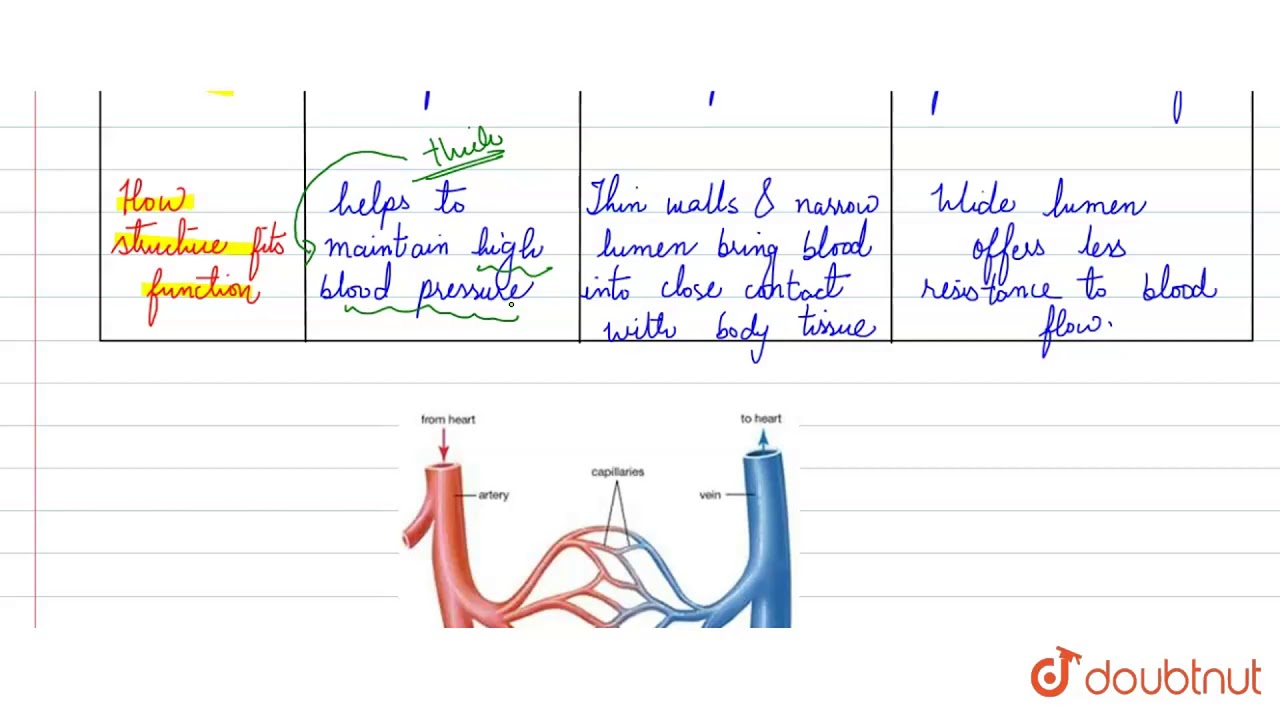
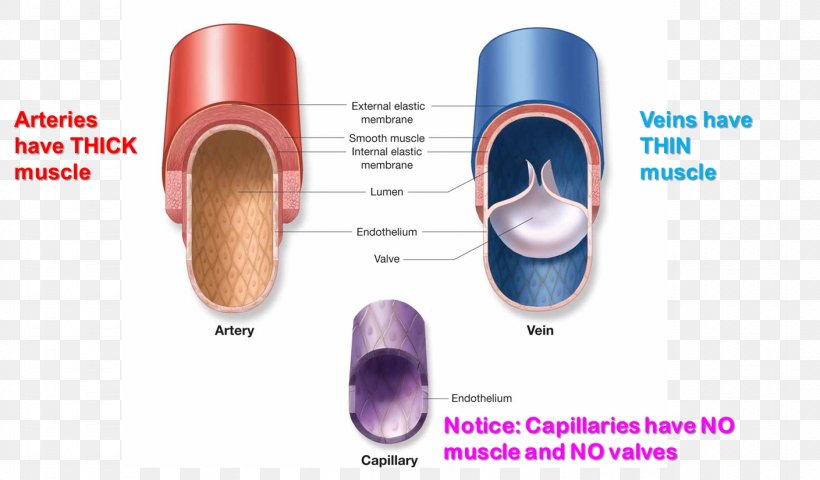
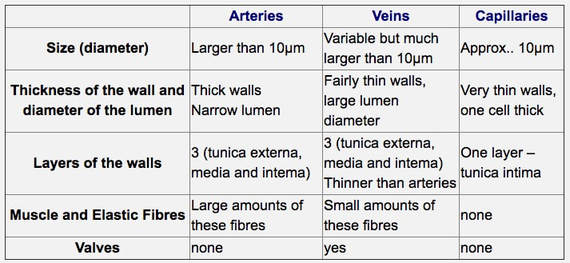
Artery Vein Have thick elastic, muscular walls Have thin, nonelastic walls Lumen is narrow Lumen is wide Carry blood from the heart to all body parts Carry blood from all body parts to the heart Carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery) Carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein) The characteristic feature of an artery can be understood better when weDiagram Roles of Circulatory System;Arteries have smaller lumens than veins, a characteristic that helps to maintain the pressure of blood moving through the system Together, their thicker walls and smaller diameters give arterial lumens a more rounded appearance in cross section than the lumens of veins Figure 2 (a) Arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much
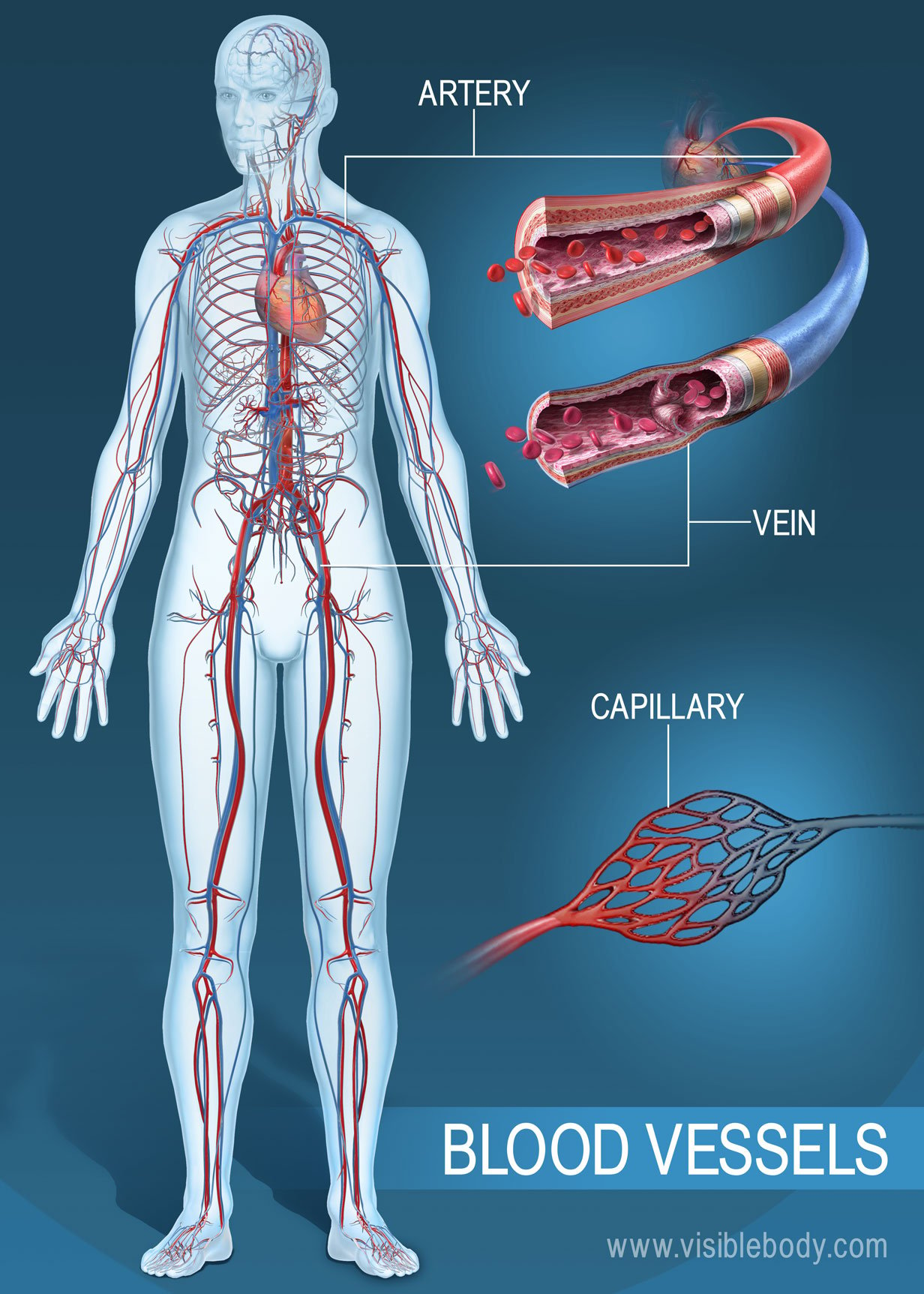



Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy
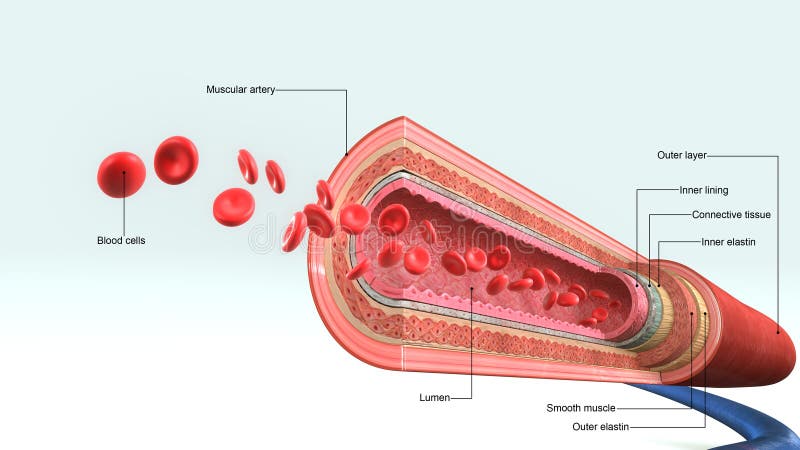



Lumen Artery Stock Illustrations 61 Lumen Artery Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Get started with our blood vessel diagrams and artery and vein quizzes Stimulation of the alpha receptors produces contraction of the smooth muscles On the contrast, stimulation of the beta receptors produces dilatation of the vessels Consequently, this allows for sympathetic regulation of blood pressure Additionally, the smooth muscle layer also secretes extracellular• When you compare an artery and a vein side by side, you observe a thick tunica media in the artery and thin walls in the vein Page 6 Systemic Pathway of Blood Through Vessels • This graphic will remind you that in the systemic circulation blood travels from the heart to elastic arteries, muscular arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, then back to the heart Page 7Arteries, veins, and the heart are the main parts of the system To understand the system, the students need to create their diagrams It can also help them in getting an overview of artery vs vein Creating a freehand diagram of arteries and veins can be troublesome The students can use online tools like EdrawMax, which can help them create



Artery Wikipedia



What Is The Function Of A Lumen In A Cell Quora
Comparave'Structure'of' Artery'and' Vein'Vessel'Walls' • Veins *1Tunica Interna* * *aEndothelium* * *b**Basementmembrane* ** *2**Tunica*MediaFeatures of Arteries and Veins (With Diagram) In this article we will discuss about the general features of Arteries and Veins Arteries and veins are main blood vessels Arteries carry blood from the heart to different body parts Veins bring blood from different body parts to the heart The veins have valves to prevent backward flow of bloodCirculatory System Artery, Vein and Capillary In this video I outline the structural and functional differences between the three blood vessels in the body
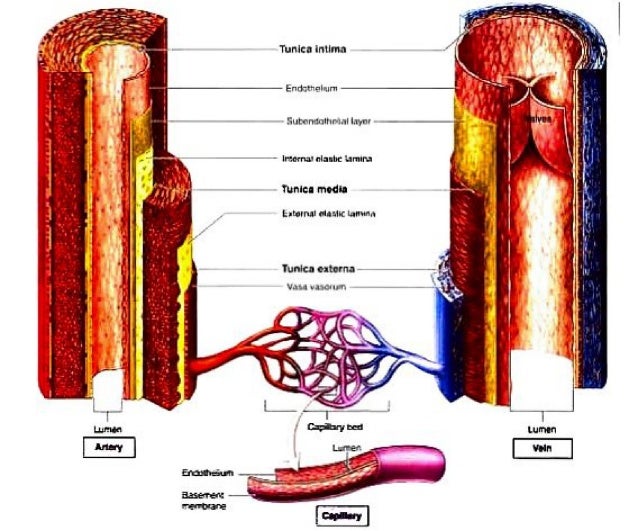



Structure And Function Of Arteries And Veins
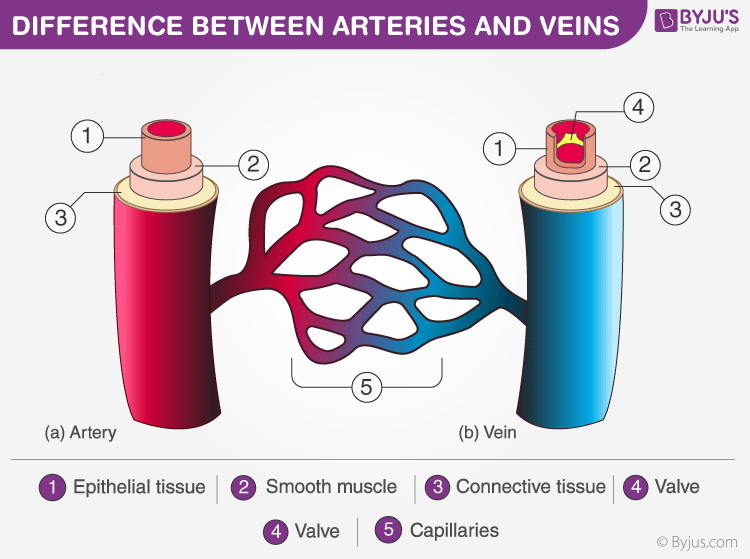



Discover Important Difference Between Arteries And Veins
Vein Veins are the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart in an even flow They have thin walls, large lumens, and valves Veins contain impure blood ie carbon dioxide mixed blood The pulmonary vein is an exception as it always carries purebloodThe velocity of blood flow slows as blood flows into smallerPractical Examination of artery and vein using a light microscope Aim To observe a cross section of artery and vein and to draw a labelled scientific diagram
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13219/arteries-and-veins.psb_english.jpg)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub



1
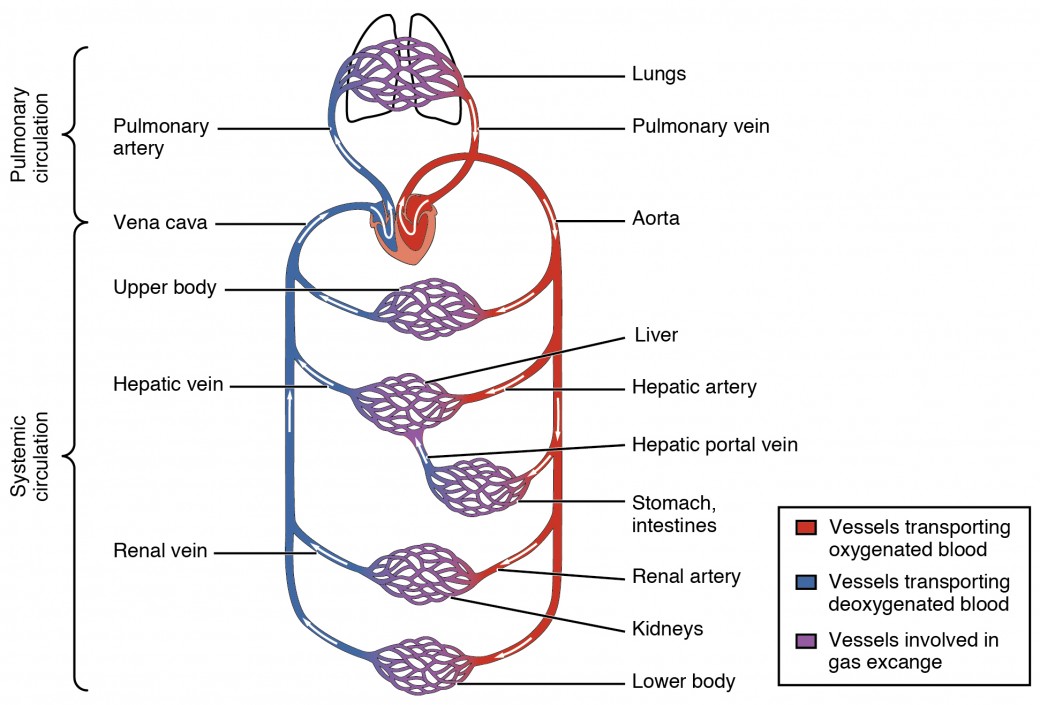
The arteriolar lumen regulates the flow of blood through the capillaries Just like the arterial system, three layers make up the vein walls But unlike the arteries, the venous pressure is low Veins are thinwalled and are less elastic This feature permits the veins to hold a very high percentage of the blood in circulation The venous system can accommodate a large volume of labelled diagram of arteries Conclusion Arteries and Veins are the major parts of the blood circulation system in any animals on the planetboth play and important role in human body alsothe main purpose of these is blood circulation but there is a slight difference between arteries and veins ie arteries are the blood vessels which take blood away from the heart to the otherArteries and veins transport blood in two distinct circuits the systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit Systemic arteries provide blood rich in oxygen to the body's tissue The blood returned to the heart through systemic veins has less oxygen since much of the oxygen carried by the arteries has been delivered to the cells In




Blood Vessels Grade 9 Understanding For Igcse Biology 2 68 Pmg Biology




Solved A Vein Possesses A Large Lumen Because
5 Comparisons of Arteries and Veins Arteries have more elastic and muscular tissue Veins have a bigger lumen Arteries carry blood at a higher pressure than veins Veins contain valves, arteries don't Arteries are usually bright red in colour, veins are usually dark redBlood is transported in arteries, veins and capillaries Blood is pumped from the heart in the arteries It is returned to the heart in the veins The capillaries connect the two types of blood Furthermore, the lumen of the artery is narrow, but in the vein, the lumen is wide Moreover, a significant difference between artery and vein is that the arteries don't have valves, but veins do have valves to prevent backflow After death, the arteries become empty, but the veins do not So, this is another interesting difference between artery and vein




Veins Bioninja



7 4 Blood Vessels Biology Libretexts
The two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placentaWe are pleased to provide you with the picture named Human Body Artery Diagram In DetailWe hope this picture Human Body Artery Diagram In Detail can help you study and research for more anatomy content please follow usIn biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine It comes from Latin lumen 'an opening' It can refer to The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows;
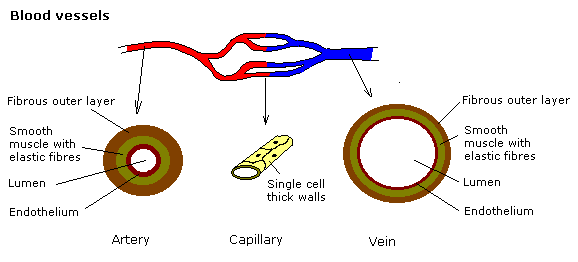



Gcse Science The Heart Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Circulatory System The Histology Guide
1 Skeletal muscle pump 2 Respiratory pump What is the speed of the velocity of blood? Artery has thick muscular walls Vein has thin muscular walls It has narrow lumen It has a broad lumen There are no valves Thin pocketshaped valves are present in the veins Arteries progressively decrease in size and branch to form arterioles Arterioles further breaks up to form capillaries Capillaries unite to form branches calledC Veins have a muscular wall to carry blood at high pressure, and arteries have valves to prevent the backflow of blood;



Http Www Oakparkusd Org Cms Lib5 Ca Centricity Domain 307 19 blood vessels Pdf
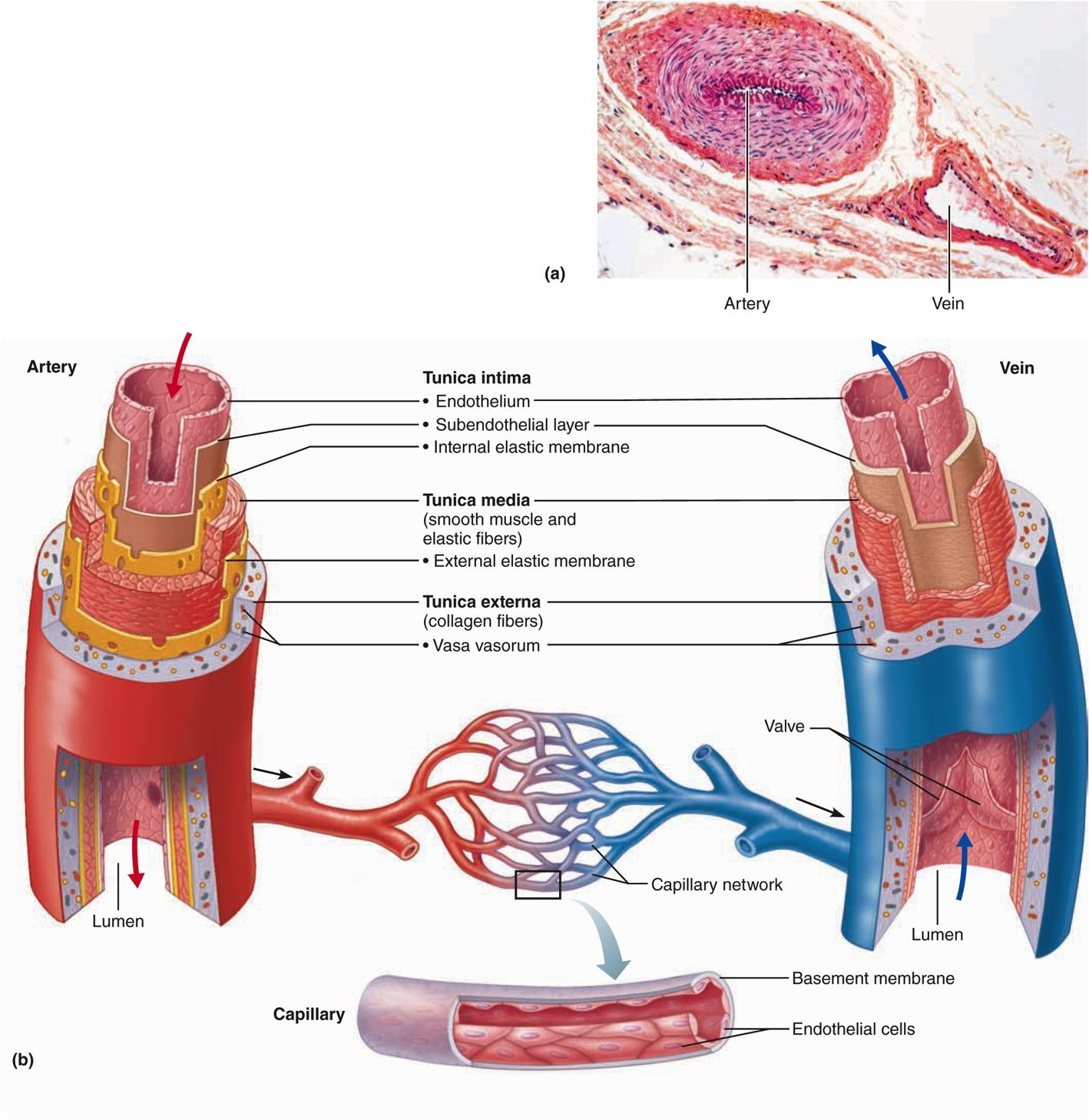



Artery Vein Artery Vein Tunica Intima Endothelium Chegg Com
Arteries possess narrow lumen Veins possess wide lumen 12 Pressure of blood flowing through the artery is high Pressure is low 13 Pulse is detectable in the artery Pulse not detectable in the vein 14 Blood flow rate is quick and rapid Blood flow rate is slow and steady 15 Blood volume is low Much higher blood volume than capillaries and arteries 16 Carry aboutAn artery (plural arteries) (from Greek ἀρτηρία (artēria) 'windpipe, artery') is a blood vessel that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc) Most arteries carry oxygenated blood;Remove any clots which may obstruct the vessel lumen 3 Arteries are small, thickwalled spiralling vessels, whilst the vein is larger and thinwalled (see diagram 4 Prime the catheter, and if reuired dilate the vessel using iris forceps (see diagram 5 Advance the catheter using short, smooth strokes Arterial Catheterisation 1 Place the catheter tip either at the upper aorta above the




Blood Vessels With Artery And Vein Internal Structure Comparison Vector Illustration Educational Lumen Direction Description Scheme Labeled Tunica Intima Media And Externa Graphic For Anatomy Study Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock
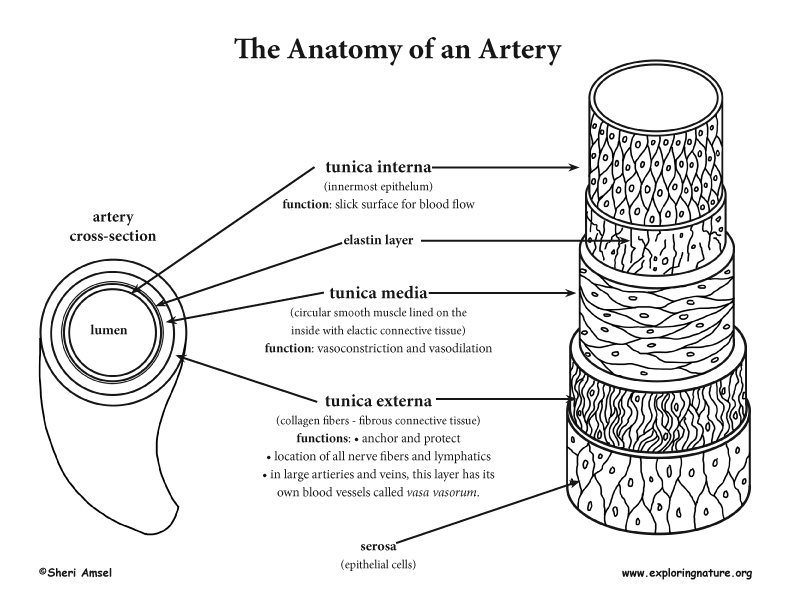



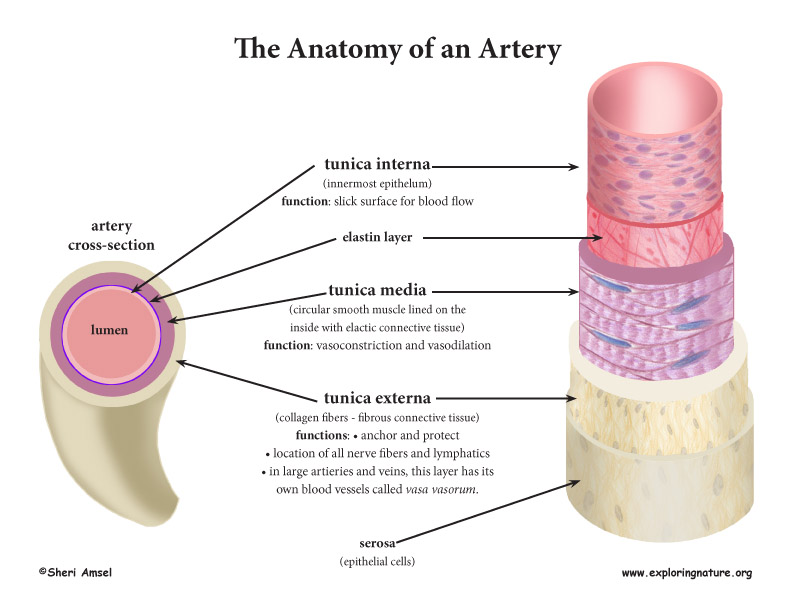
Blood Vessel Anatomy Advanced
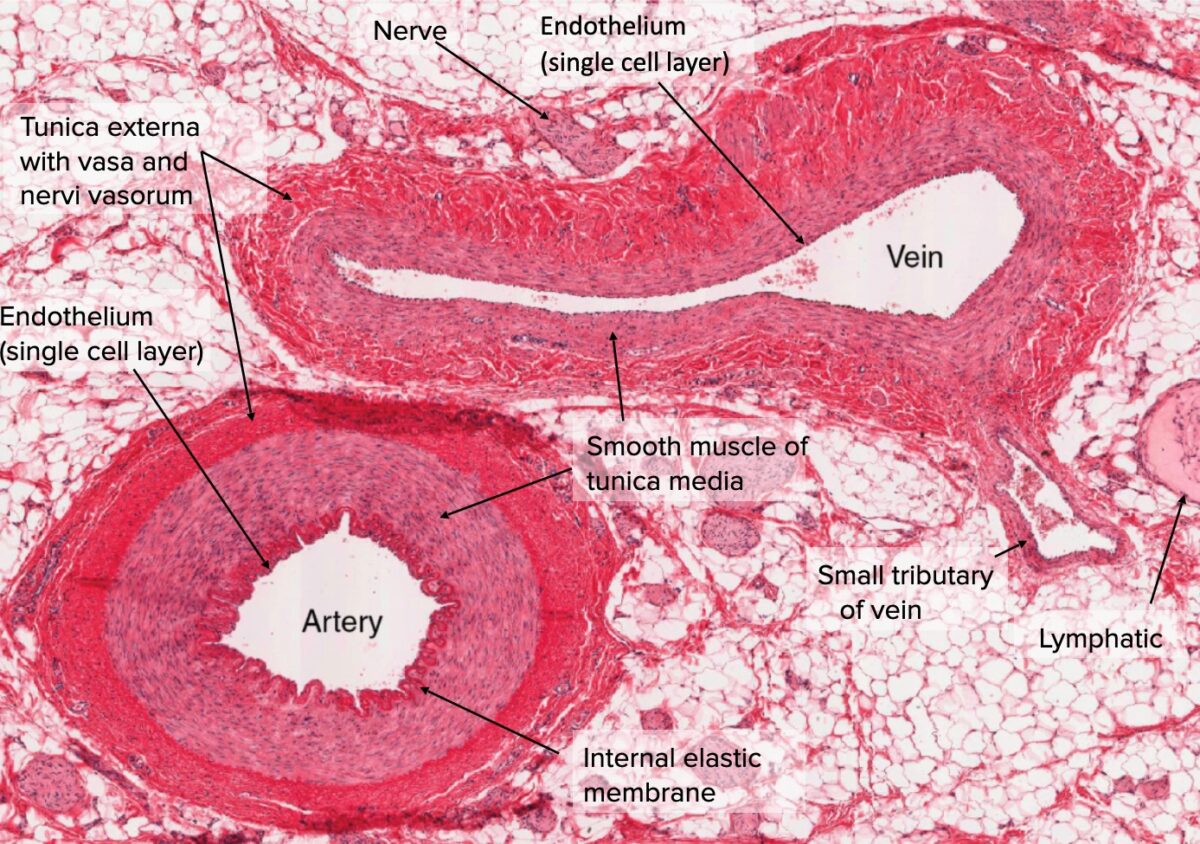
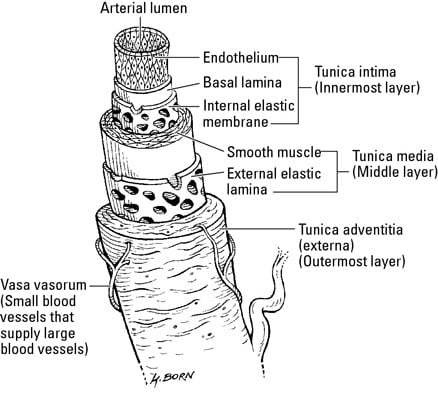
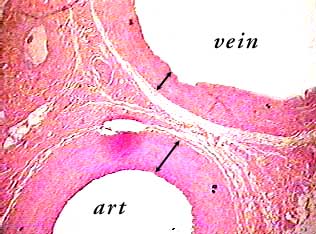
This is a diagram of a medium sized muscular artery The lumen colored in red is lined by the intima (1 and 2) A single layer of squamous epithelium called the endothelium (1), is supported by the connective tissue and the internal elastic membrane of the basal lamina (2) The tunica media is made of smooth muscle(3) and the external elastic membrane (4) Variable amounts o elastinPopliteal artery, and there would be matching veinsLearn the differences between these blood vessels!




Blood Vessels Diagram Quizlet




Anatomy Physiology Ii Chapter The Circulatory System Blood Vessels And Circulation Diagram Quizlet
Vein Page 2 of 3 Developed by Madeleine Cox Answers Answers Endothelium Artery Vein Lumen Endothelium Smooth muscle and elastic tissue Fibrous tissue Endothelium Smooth muscle and elastic tissue Fibrous tissue Valves Lumen Lumen Smooth muscle and elastic tissue Valves Fibrous tissue Artery Endothelium Lumen Smooth muscle and elastic tissue Fibrous tissue Created Lumen These possess narrow lumen These possess wide lumen 7 Pressure Blood flows under high pressure Blood flows under low pressure 8 Color These are reddish in color These are bluish in color 9 Types Pulmonary and systemic arteries Superficial veins, deep veins, pulmonary veins and systemic veins 10 Internal Diameter NarrowerProvides nutrients essential for hematopoiesis and building hemoglobin Endocrine Delivers hormones atrial natriuretic hormone (peptide) secreted by the heart atrial cells to help regulate blood volumes and pressures




Blood Vessels Grade 9 Understanding For Igcse Biology 2 68 Pmg Biology



Www Palmbeachstate Edu Slc Documents ndpch19lecturepearson Pdf
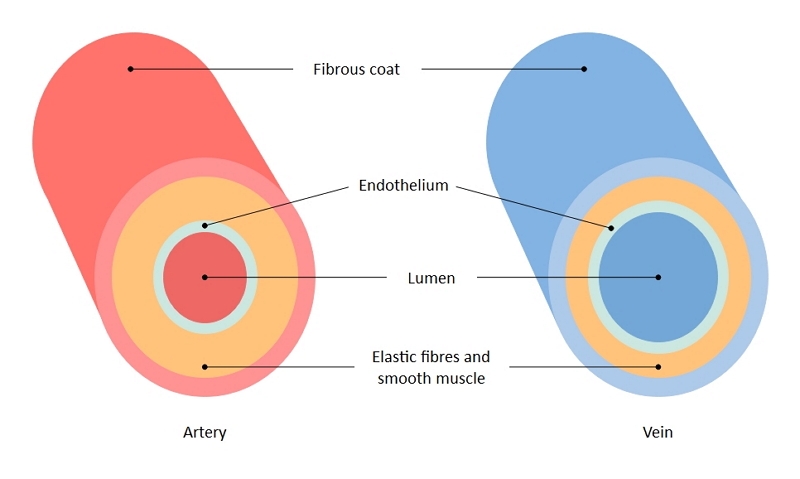
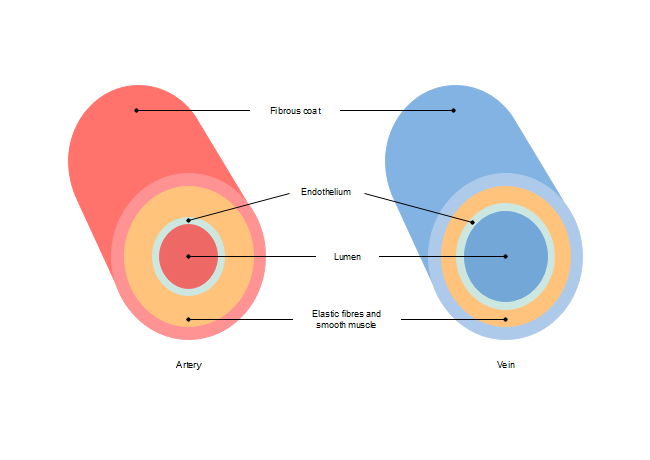
The ArteryVein diagram is created in EdrawMax and it mainly shows the main features of both Artery and Veins, ie, the fibrous coat, endothelium, lumen, and elastic fibers The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels Whereas, Lumen is the inside space Blood circulation principal veins and arteries diagram In this image, you will find the internal jugular vein, common carotid artery, subclavian vein, superior vena cava, axillary artery, pulmonary vein, brachial artery, inferior vena cava in it You may also find the hepatic vein, portal vein, radial artery, ulnar artery, superior mesenteric Artery and vein diagram lumenGI radiological anatomy Abdominal vessels This has two modules Learning Module To review the content of the subject UNDER CONSTRUCTION Self assessment module You should use this module only after you have read textbooks or have knowledge of the subject and are ready to see whether you have comprehended the subjectStart




Heart And Circulation




Structures Of Blood Vessels A Level Biology Revision Notes
They are just alike arteries except dural sinuses and hepatic portal circulation 13 the blood pressure in side arteries is high in veins, the blood pressure is low 14 they distribute blood to body organs collect blood from body organs 15 arteries have small lumen the veins have large lumen 16 spurty or fast movements of blood withD Arteries have a muscular wall to carry blood at high pressure, and veins have valves toThe pathways of the bronchi in the lungs



Arteries Concise Medical Knowledge




Vessel Comparison Bioninja
A Both arteries and veins have thick muscular walls to carry blood at high pressure; Our LATEST youtube film is ready to run Just need a glimpse, leave your valuable advice let us know , and subscribe us!The liver is supplied by two main blood vessels on its right lobe the hepatic artery and the portal vein The portal vein brings venous blood from the spleen, pancreas, and small intestine so that the liver can process the nutrients and byproducts of food digestion Bile The bile produced in the liver is essential for the digestion of fats Bile is formed in the liver, and it is stored in




Blood Vessel Wikipedia



Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Veins A vein is a blood vessel that conducts blood toward the heart Veins have thinwalls, and compared to arteries, large and irregular lumens Venules are the smallest veins that form when capillaries merge together Veins are categorized differently than arteries and capillaries, but can be broken down into four other subtypes PulmonaryHUBS 192 Lecture 4 – Circulatory System Anatomy Arteries and veins Vessels Diagram What vessels would RBC pass through on the journey from left side of heart to foot or hand and back to right side of heart towards foot – aorta, thoracic aorta;The question is what causes ulcers to form, not what causes venous




Blood And Blood Vessels Info Pdf Pages 1 2 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




27 Differences Between Arteries And Veins Arteries Vs Veins
Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy These videos do not provide m Arteries and veins are two of the body's main type of blood vessels These vessels are channels that distribute blood to the body Learn



Draw A Well Labelled Diagram Of Ts Of Artery And Ts Class 11 Biology Cbse



1




Artery Wall An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Pin On Human A P




1 Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy Physiology



Capillaries And Veins Returning Blood To The Heart Dummies



Diagram Diagram Of Blood Vessel Slide Full Version Hd Quality Vessel Slide Diagrampress Newsymposium It




Artery And Vein Lumen Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Capillary Outgrowths From Mouse Arteries And Veins Contained Open Download Scientific Diagram




How To Draw The T S Of Artery And Vein Human Physiology Body Fluids And Circulation Cbse Isc 11 Youtube



Artery And Vein Cross Section High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Blood Vessels And The Heart Fabioclass



A Guide To Understand Artery And Veins With Diagrams Edrawmax Online




Arterial And Venous Systems Arteries Arterioles Venules Veins Circulatory System Mcat Content



Histology Of Blood Vessels



Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii



State The Differences Between Artery Vein And Capillary Youtube




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii




How Would You Compare The Structures And Functions Of Arteries Capillaries And Veins Socratic




Artery And Vein Histology Osmosis



Artery And Vein C S




Principles Of Human Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 18 Blood Vessel And Circulation



Blood Vessel Anatomy Advanced



Free Artery Vein Diagram Templates




The Diagram Given Below Represents The Human Heart In One Phase Of Its Functional Activities Study The Same And Answer The Questions Which Follow I Name The Phase Ii Label The Parts 1 2




Lumen Anatomy Wikipedia




Long Answer Question Describe Histological Structure Of Artery Vein And Capillary Biology Shaalaa Com




Blood Vessels The Cardiovascular System




Ch 31 Test Prep For Ap Courses Biology For Ap Courses Openstax




What Is The Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Ppt Download




Blood And Blood Vessels Info Pdf Pages 1 2 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



14 4 Blood Vessels Human Biology



1



Difference Between Veins And Arteries Definition Features Function
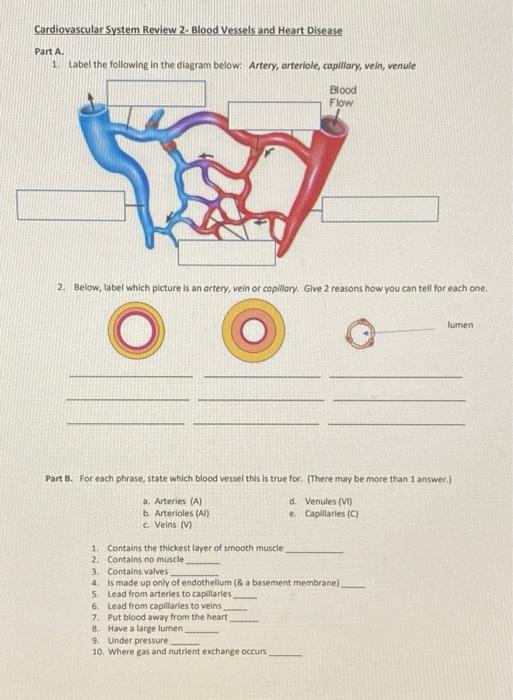



Cardiovascular System Review 2 Blood Vessels And Chegg Com



Capillary Pulmonary Artery Vein Function Png 1409x5px Capillary Anatomy Artery Blood Blood Vessel Download Free




Why Are The Pulmonary Veins Called Veins If They Carry Oxygenated Blood Why Are Pulmonary Arteries Called Arteries If They Carry Deoxygenated Blood Socratic



1



Differences Between Artery And Vein




Artery Vs Vein Biology Dictionary
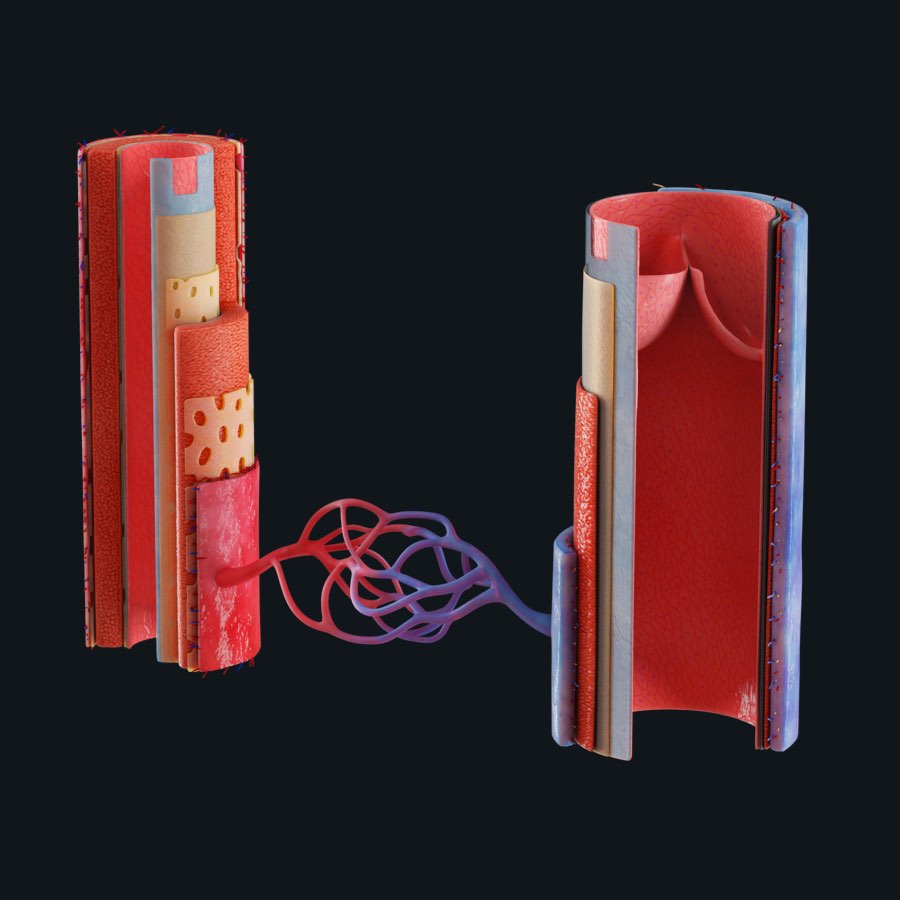




Blood Vessels The 60 000 Mile Network Inside Us Anatomy Snippets Complete Anatomy
/GettyImages-87394349-568952ca3df78ccc152e5be5.jpg)



Pulmonary Artery Anatomy Function And Significance




In Anatomy What Is A Lumen With Pictures




A And P 2 Chapter 19 Flashcards Quizlet



Difference Between Arteries And Veins



Topic 6 2 The Blood System Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Figure 37 1 Artery And Vein Diagram Quizlet
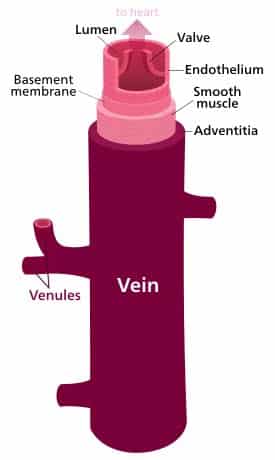



Ultrastructure Of Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Teachmeanatomy
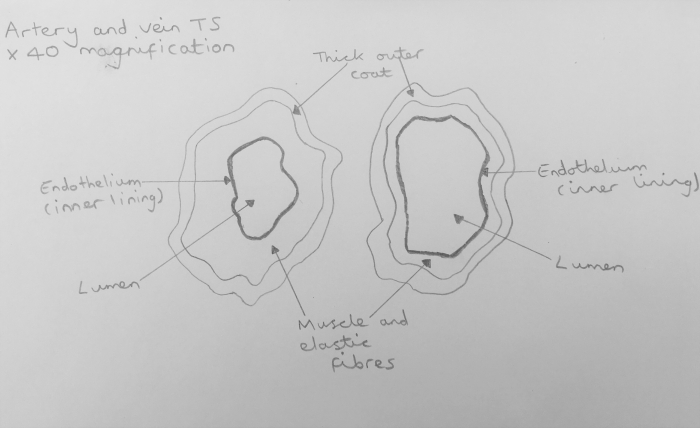



Study Arteries And Veins With A Microscope Worksheet Edplace




Lumen Artery Stock Illustrations 61 Lumen Artery Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



14 4 Blood Vessels Human Biology




Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
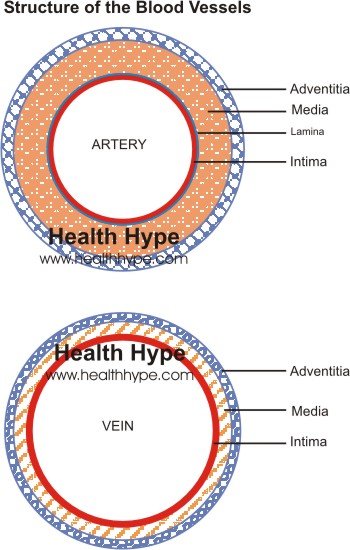



Thickened Arteries And Veins Causes Of Blood Vessel Thickening Healthhype Com




Blood Vessel Composition Large Blood Arteries And Veins Vessels Are Download Scientific Diagram



Http Www Usdbiology Com Swanson Anat Rosenfeld Arteries and veins Pdf
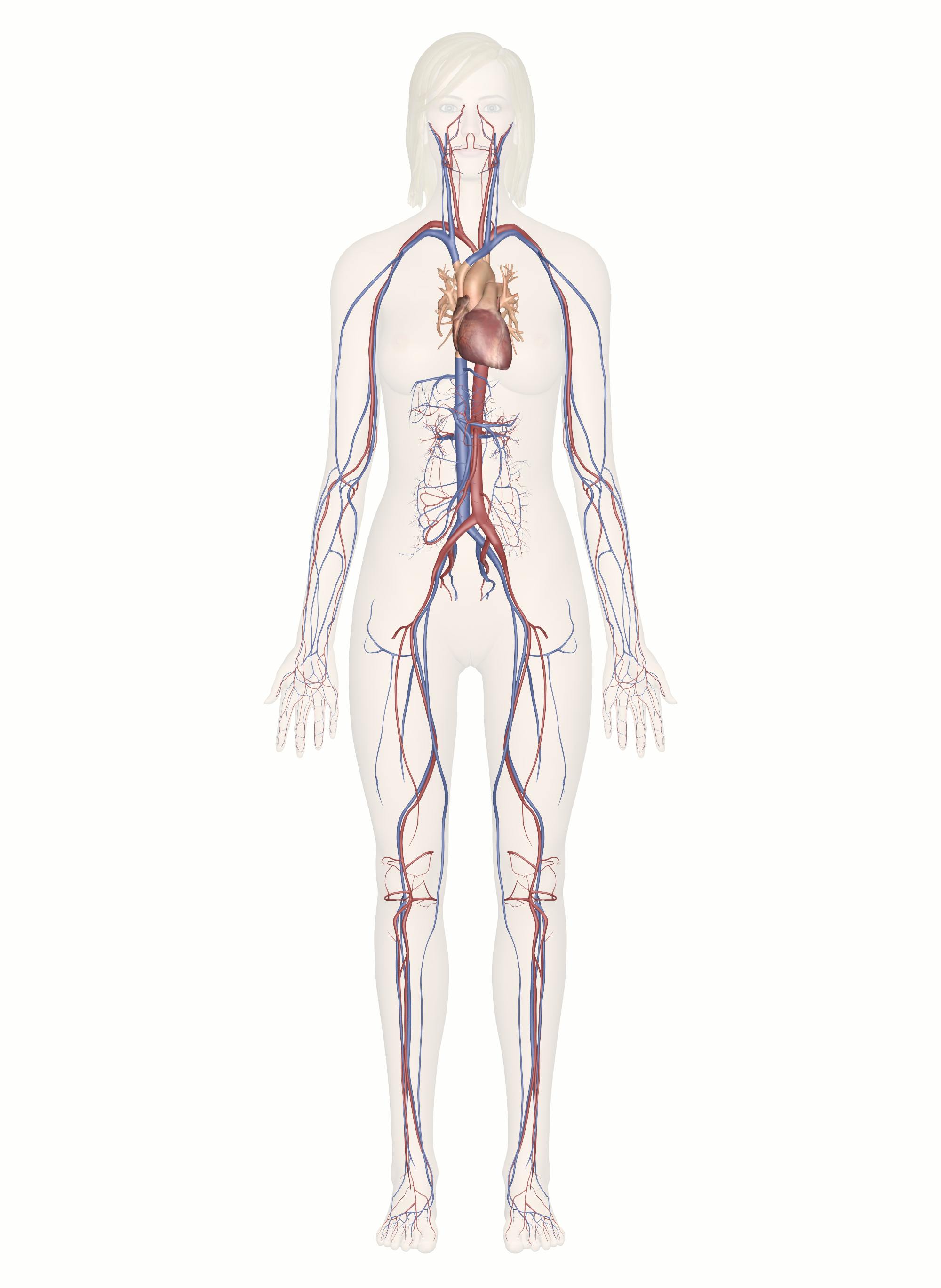



Cardiovascular System Human Veins Arteries Heart




2 65 Describe The Structure Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries And Understand Their Roles Saturnine Notes




Vein Function Structure Anatomy Types Of Veins Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Vessel Comparison Bioninja




Medical School Cross Section Of An Artery Vein And Capillary Physical Education Lessons Arteries Arteries And Veins




Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy



Difference Between Artery And Vein Difference Between




Blood Vessels Gcse Biology 9 1 Youtube




A Significant Increase Arterial And Venous Lumen Diameter Was Observed Download Scientific Diagram



Artery Vein 1



Www Mccc Edu Falkowl Documents Cardiovascularsystem Pdf



What Is The Structure Of The Lumen In The Veins Quora



Apii Notes Home Page




Artery Lumen Stock Illustrations 61 Artery Lumen Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Valve Capillary Network Lumen Vein Lumen Artery End




Difference Between Arteries And Veins Guidance Corner




A Patent Vessel Lumen In Control Group Artery Anastomosis 100 He Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿